Investing in the stock market can be intimidating, especially with the myriad strategies available. Two of the most popular methods are fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Each approach has unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of investors and market conditions. This article will help you understand when to use fundamental analysis versus technical analysis, making your investment decisions more informed and strategic.

Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company's financial health and performance to determine its intrinsic value. This method focuses on various factors such as earnings, revenue, assets, liabilities, and overall economic conditions. The goal is to assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its current market price.
Financial Statements: Analysts scrutinize the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to gauge a company’s profitability, debt levels, and cash management.
Ratios and Metrics: Key metrics include the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio, Return on Equity (ROE), and Earnings Per Share (EPS). These ratios help compare a company's performance to its peers and historical data.
Industry Analysis: Understanding the industry context is crucial. This includes market trends, competition, and regulatory environment.
Economic Indicators: Economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth impact a company's performance and, consequently, its stock price.
Long-Term Investing: Fundamental analysis is essential for long-term investment in a company. It helps identify stocks with strong growth potential and solid financials.
Value Investing: Fundamental analysis is a go-to strategy for investors like Warren Buffett, who seek undervalued stocks with the potential for significant appreciation.
Income Investing: Those focused on dividend stocks benefit from fundamental analysis by selecting companies with sustainable dividend payouts.
Technical analysis, on the other hand, involves studying past market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements. This method relies on charts and patterns to identify trading opportunities based on historical performance.
Price Charts: Candlestick, bar, and line charts are commonly used to represent price movements over different time frames.
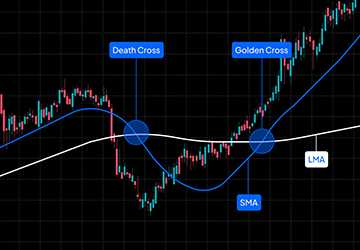
Indicators and Oscillators: Tools like Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) help identify trends and potential reversals.
Patterns: Analysts look for patterns such as Head and Shoulders, Double Tops and Bottoms, and Flags and Pennants to predict future price action.
Volume Analysis: Changes in trading volume can indicate the strength or weakness of a price move, providing clues about potential reversals or continuations.
Short-Term Trading: Technical analysis is essential if you focus on short-term gains, like day trading or swing trading. It helps pinpoint entry and exit points for trades.
Market Timing: For those aiming to time the market to maximize profits, technical analysis provides the necessary tools to gauge market sentiment and momentum.
Trend Following: Traders who prefer to follow market trends can use technical analysis to ride ongoing trends and avoid unfavourable market conditions.
While fundamental and technical analysis are often seen as distinct strategies, combining them can offer a comprehensive market view.
Confirming Trends: Use technical analysis to confirm trends identified through fundamental analysis. For instance, if a company’s strong financials suggest a buying opportunity, technical indicators can help pinpoint the best time to enter the trade.
Risk Management: Fundamental analysis helps identify the quality of an investment, while technical analysis assists in managing risk through precise entry and exit points.
Diversification: Applying both methods can diversify your investment strategy. For example, long-term investments might be selected based on fundamentals, while technical signals can guide short-term trading.
Suppose you are interested in investing in a tech company.
Fundamental Analysis: You start by analyzing the company's financial statements and assessing its revenue growth, profit margins, and R&D investments. You also consider industry trends, such as the demand for cloud computing services.
Technical Analysis: Once you decide the company has strong fundamentals, look at its price charts. You notice a recent breakout from a consolidation pattern, supported by high trading volume. The RSI indicates the stock is not overbought, suggesting a good entry point.
Consider a scenario where you want to trade a volatile biotech stock.
Technical Analysis: You analyze the stock's price movements, identifying a bullish flag pattern. The MACD crossover indicates a potential upward move, and increasing volume supports this prediction.
Fundamental Analysis: To manage risk, you review the company's latest earnings report and pipeline developments. Positive news about a new drug approval adds confidence to your technical analysis, reinforcing your buying decision.
Understanding market sentiment and economic cycles is essential to choosing between fundamental and technical analysis. Market sentiment reflects the overall attitude of investors toward a particular security or market. During periods of optimism, prices may rise regardless of fundamentals, making technical analysis helpful in identifying entry points. Conversely, in times of pessimism, prices drop even if a company's fundamentals are strong, providing opportunities for value investors.
Economic cycles also play a crucial role. In a booming economy, stocks often perform well, and technical analysis can help spot short-term gains. During economic downturns, fundamental analysis helps pinpoint companies with robust balance sheets that can endure tough times.
Choosing between fundamental and technical analysis depends on investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. Long-term investors seeking value or income benefit more from fundamental analysis, while short-term traders focused on market timing find technical analysis more useful. Understanding each approach's strengths and limitations helps make informed investment decisions.
Combining both methods often provides a well-rounded strategy, enhancing your ability to navigate the stock market confidently. Invest wisely, and remember that no strategy guarantees success. Continuous learning and adapting to market changes are essential for becoming a successful investor.